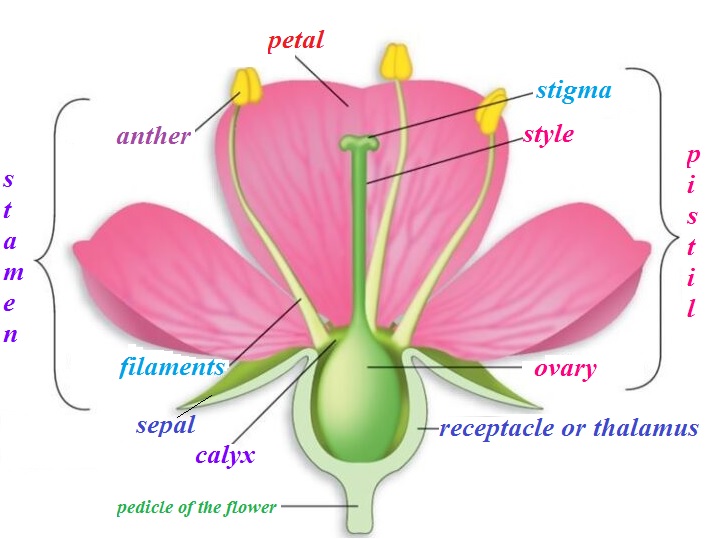
The flower is a modified shoot, meant for sexual reproduction. A flower has four main parts i.e. Calyx and Corolla (as accessory organs) and Androecium and Gynoecium (reproductive organs). All these parts are arranged in a cyclic manner on the thalamus. Thalamus or receptacle: A swollen end of the stalk or pedicle of the flower.
In some flowers like lily, the calyx and corolla are not distinct and are termed as perianth.
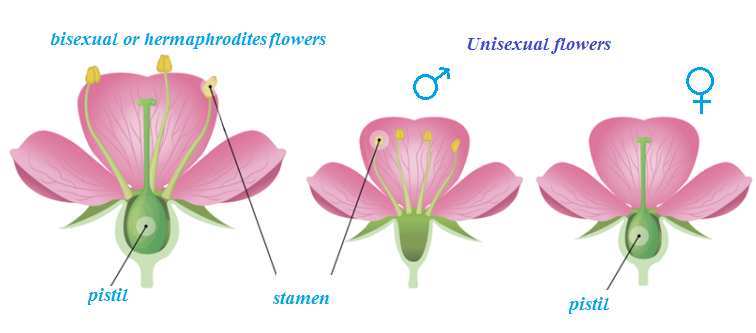
A Flower with only one kinde reproductive organ either stamen or pistil is unisexual.
Flowers with both of these organs (stamen and carpel) are present is called bisexual or hermaphrodites.
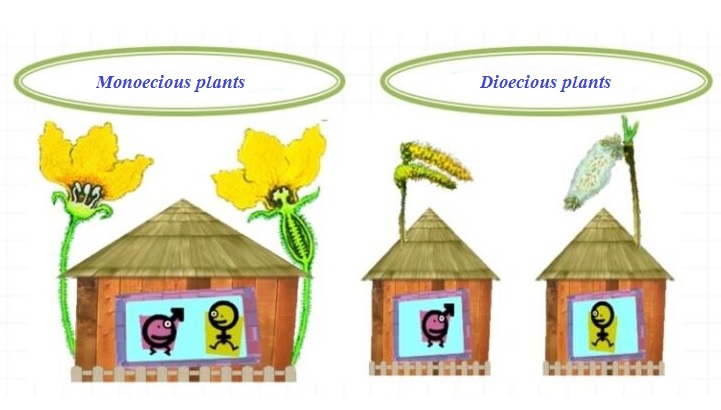
MONOECIOUS OR DIOECIOUS PLANTS?
Sometimes, female and male flowers are on the same plant, so such plants are called monoecious; or on different plants, such plants are called dioecious. For example, pumpkin, birch, corn are monoecious plants. Poplar, willow, hemp are dioecious plants.
Symmetry of Flower
The number, shape, size, and arrangement of floral leaves in a flower determine the symmetry. Following types of symmetry found in flowers:
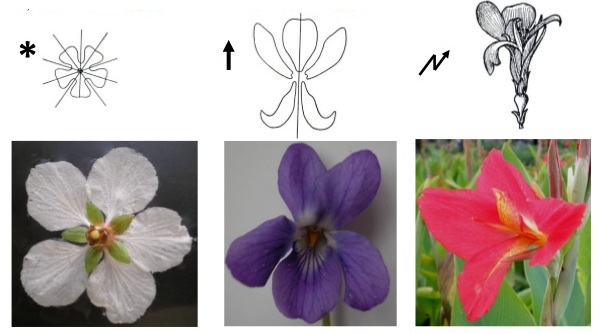
- Actinomorphic (radial symmetry): When a flower can be divided into two equal radial halves in any radial plane passing through the center, it is said to be actinomorphic, e.g., mustard, datura, chili.

- Zygomorphic (bilateral symmetry): In this type the flower can be divided into two similar halves only in one particular vertical plane, it is zygomorphic, e.g., pea, Gulmohur, Bean, Cassia.

- Asymmetric (irregular): If the flower cannot be divided into two similar halves by any vertical plane passing through the center it is called an Asymmetric flower. e.g. Canna

CAROLLA
It is the second whorl of flowers and made up of Petals that are usually brightly colored to attract insects for pollination. Corolla with free petals is called polypetalous, and corolla with fused petals is called gamopetalous.
The forms of corolla:
Cruciform: It consists of 4 petals arranged crosswise, each petal is clawed. e.g. mustard, so the name of the family is Cruciferae.
Caryophyllaceous: it consists of 5 petals, each with a comparatively long claw and the limbs of petals are placed at the right angles to the claw, e.g. Dianthus.
Rosaceous: it consists of 5 petals, with short claws or none. The limbs spread regularly outwards e.g. Rosa indica.
Campanulate or Bell-shaped: the shape of the corolla is like a bell. e.g. Physalis.
Tubular: Corolla is tubular or cylindrical and gamopetalous. e.g. Disc floret of Helianthus sp.
Infundibuliform or Funnel-shaped: Corolla is in shape like a funnel, e.g. Datura
Rotate or wheel-shaped: the tube of corolla is found narrow and short and the limbs are right angles to the tube e.g. Solanum melongena (Brinjal).

TYPES Of INFLORESCENCE
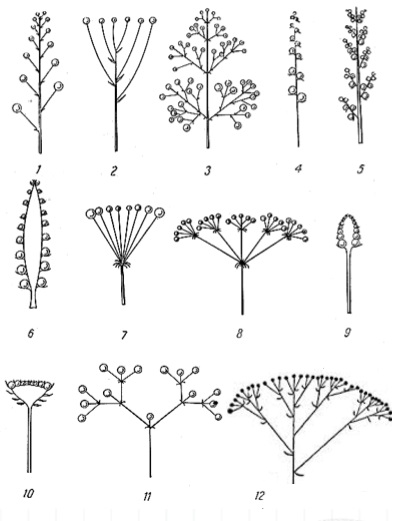
- 1. Raceme
- 2. Corymb
- 3. Panicle
- 4. Spike
- 5. Catkin
- 6. Spadix
- 7. Umbel
- 8. Compound umbel
- 9. Head
- 10. Capitulum
- 11. Dichasial cyme
- 12. Compound corymb
Sexual reproduction in flowering plants (Angiosperms)
Androecium – consisting of stamens, Gynoecium or pistil – consisting of carpels. Stamens and pistil found in flowers are the reproductive parts that contain germ cells.
Stamen: is the male reproductive part of the flower and it produces pollen grains that are yellowish in colour.
The pistil: It is present in the center of a flower and it is the female reproductive part.
The pistil is made up of three parts: the swollen bottom part is the ovary, the middle elongated part is the style, the terminal part which may be sticky is the stigma.
Ovary and Ovules: the ovary contains an ovule and there is one egg in each ovule.
Pollination– Transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of a flower may follow various ways. for example- Pollination by wind, Pollination by insects (Entomophily), Pollination by Water (Hydrophily), Pollination by Animals (Zoophile). Pollination may be of two types:
- Self-pollination-transfer of the Pollen grains to the stigma of the same or from another flower on the same plant. Ex. pea and gram.
- Cross-pollination-transfer of Pollen grains from a flower to the stigma of another flower of another plant of the same species Ex. palm and maize.
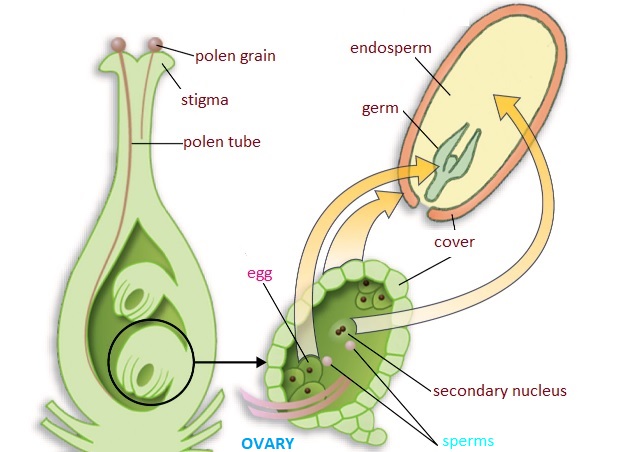
FERTILIZATION
In flowers, the process of fertilization initiates as after the pollen comes on a suitable stigma, it has to reach the female germ cells which are in the ovary. For this, a tube grows out of the pollen grain and travels through the style to reach the ovary.
Fertilization of flowering plants include:
- Each pollen grain forms a small tube-like structure called a pollen tube which emerges through the germ pore.
- The pollen tube grows through the tissues of the stigma and style and finally enters the ovule through the micropyle.
- Here two types of fusion, syngamy, and triple fusion take place in an embryo sac, the process is termed double fertilization. After triple fusion, the triploid primary endosperm cell develops into an endosperm.
- It Gives stimulus for the growth of the ovary, leading to fruit formation.
After fertilization– Events found are the development of endosperm and embryo and maturation of the ovule into seed and ovary into a fruit. i.e. ovule makes seed and ovary make fruits.
The seed contains the future plant or embryo which develops as a seedling under appropriate conditions and the process is known as germination