The root is a negatively phototropic and descending cylindrical axis of a plant that develops from the radicle of the embryo.
These provide anchorage for the plant, take in water and nutrient which helps the plant to grow.
Root has several functions : absorbs water and minerals from soil, binds plant to the ground, stores food. Root has several regions.
They are:
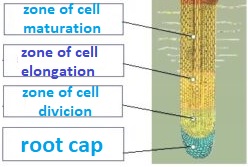
Root cap: it is found at the end, protects root,
Zone of cell division (apical meristem): cells divides rapidly and growth.
Zone of elongation: cells get longer and this part of root also gets longer.
Zone of differentiation(maturation): cells complete their differentiation, cells increase in width, also root hair are found.
Epidermis outermost layer of root. It covers and protects the root. Root hair: increase the surface area of root for absorption of water and minerals. Cortex is a part between cylinder the epidermis and vascular cylinder. It supports root and stores food. Endodermis is the layer of cells outside of cylinder. Water cannot pass between the cells of endodermis so it must fist enter the cell of endodermis, then pass to vascular cylinder. Vascular cylinder is central part of root. It is composed of xylem and phloem.

Root system type
The main functions of the root system are the absorption of water and minerals from the soil, providing proper anchorage to the plant parts, storsng reserve food material and synthesis plant growth regulators.
- Formation of theprimary root by the direct elongation of radicle in most dicotyledonous plants. It grows inside the soil. It bearslateral roots of several orders, which are called secondary, tertiary, etc. roots.
- As can be seen in the example of mustard, the primary roots and their branchers constitute the tap root system.
- Monocotyledonous plants have short-lived primary roots that are replaced by a large number of roots that originate from the base of the stem and constitute a fibrous root system, as seen in wheat.
- The roots arise from parts of the plant other than the radicle and are called adventitious roots. In some plants such as grass, monstera and banyan tree.
Modification of Tap Root
Conical-the root base is wide, the tapering apex and the fleshy basal part are visible-Сarrot.
Fusiform– the middle part is swollen, the apex narrows, secondary root extends from the apical region-Radish.
Napiform-The base found thick, root suddenly tapers towards the apex-Turnip.

Modification of Adventitious Roots
Tuberous-tuber like, no specific shape or size- Mirabilis.
Nodulated (tuberculated)–nodules on primary secondary roots. The ability to fix atmospheric N2-Peas.
Respiratory roots (pneumatophores)– functions to gas exchange in aerobic respiration-Mangroves.

Modification of Root For Mechanical Support
Stilt root–arises from the stem, enters in soils, consisting of many root caps. Functions for aditional support, absorption of water and minerals from the soil-Pandanus.
Clinging Roots – arises from nodes and internodes in week stemmed plants these observed in epiphytes or space parasites. Function for climbing, additional support-Ivy.
Buttress roots- these are large wide roots that arise from the basal part of the stem, spreads in the soil in various directions. Works for support-Almond and Peepal.



















